Encryption
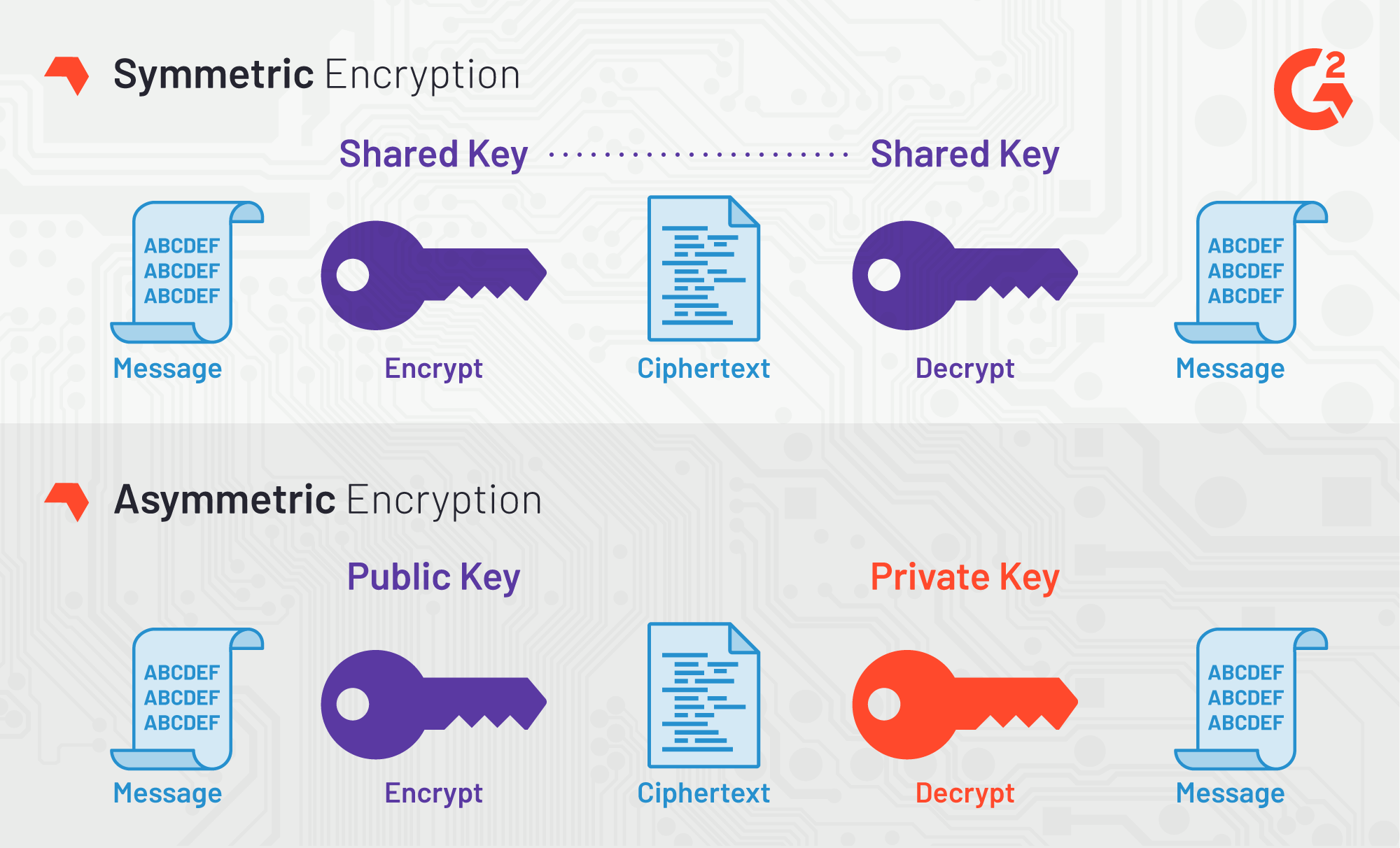
How does it work?
Encryption is the process of converting plain text into ciphertext using 1 or more keys depending on the type of encryption.
Symmetric encryption works by using a single key. This key holds the instructions to scramble the plaintext and make it unreadable and can only be deciphered by the same key. On the other hand, asymmetric encryption works with 2 keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt the data and the private key, specific to an individual, is used to decrypt it. This is useful in sending messages to another person as an interceptor wouldn't be able to decrypt the data.
Uses
The primary use of encryption is in data protection for storage. It can protect the data stored for a long time. Even if the storage is found or stolen, the data will still be unreadable without the decryption key. This is useful when storing very sensitive information as it acts as a failsafe. Similarly, it is used when moving data as if it is intercepted, it still can not be read. Another use is when a company or organization is holding a user's data. It must be secure in order to prevent identity theft, selling of data or other information that could lead to blackmail.
Why is it needed?
Encryption is necessary in all aspects of our digital life. It allows us to converse with friends and family without other prying eyes monitoring what you write. Issues of national security is kept safe and your own privacy is also ensured.
Cybercrime is an ever-increasing threat to important government documents. By accessing this data, governments can be put in a very detrimental position of vulnerability, especially if the data includes army tactics, plans of attack or other sensitive information that any enemies shouldn't have access to. Not only is it a threat to them, but it is also a threat to the general public. Hackers can steal information about you in the attempt to steal your identity, blackmail you or simply sell your information on to another person with ill-will. This is why it is extremely important for cryptographers (people experienced in creating encryption algorithms) to improve on or make new algorithms that are secure.